|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
2nd Century: Romans settle the Iberian peninsula and find some Jewish families already there, some claiming to be descendants of King David who arrived after the destruction of the first Temple or during the time of Solomon and Nebuchadnezzar. Synagogues are built in the Empire's major cities. Castile is used for pastureland, as it will be used by the Visigoths and Muslims until the Christian conquest ends the wars and agriculture can be practiced safely.
551: The Visigoths establish their kingdom on the peninsula, making Toledo their capital.
570-636: Isidore of Seville writes Etymologies (or Origins), a thorough enclopedia of in Latin, mostly based on Greek and Roman works.
587: The Visigoth King is converted to Roman Catholicism. The Kingdom is converted two years later.
613: Christian Visigoths give Iberian Jews a choice between conversion or emigration. Jews number in the "many thousands". They are economically successful but are not warriors.
632: Death of Mohammed, founder of Islam. Many Arabs and other North Africans become Muslims.
694: Remaining Jews are enslaved to serve Visigoths.
711: Muslim forces under Emir of Damascus, Tariq ibn Ziyad, enter Spain from Africa, perhaps by the invitation of Count Julian of the Visigoths. They are welcomed and aided by the Jews as liberators. In Muslim-freed territories, Jews are freed from slavery and allowed to form their own communities. Since the Muslim invaders are all men, they take Spanish (Christian) wives.
718: Muslims control almost all of al-Andalus, but are defeated in Alcama in the neighborhood of Covadonga by Pelayo, a Christian Visigoth who has been elected king. Asturian and Cantabrian mountaineers, Hispanic non-Visigoths, continue to fight the Muslims in what will be called La Reconquista (the Reconquest), even though it was not a return of the Visigoth kings. During the wars between Christians and Muslims, Jewish courtiers are valued as diplomats, translators, and advisors to both sides.
732: Muslim advance into Europe is stopped by Charles Martel at Poitiers (France). The frontier buffer between France and Muslim Spain later created by Charlemagne is called the Marca Hispanica.
756: Abd al-Rahman, Muslim commander of al-Andalus Muslims, proclaims himself Emir (king) of Cordoba. Christian strongholds in the north become the feudal holdings of the Muslims. The Andalusian economy is based on a currency of Cordoban coinage. Cordoba grows to 100,000 inhabitants - the greatest city in Europe of its time.
791 to 842: Alfonso II, Christian King of Castile, conquers a number of strongholds and settles the lands south of the river Duero.
800: Ptolemy's works are translated into Arabic by Muslim scholars, influencing philosophy and theology in Spain. In the next century literature thrives in Hebrew and Arabic, while Latin scholarship declines, even among ecclesiastics.
813: The grave of James the Apostle is "discovered" near Santiago, beginning the cult of St. James that would unite Iberian Christians of many different petty kingdoms in a single national faith. As patron saint of Spain, his cult will inspire many Christian victories against the Muslims.
929: Hisdai ibn Shaprut appointed director of customs, diplomatic emissary, and physician to Caliph 'Abd al-Rahman. He creates a center for spiritual studies for Spanish Jews, and founds a yeshiva (school) headed by Moses ben Hanokh. The cultural center supports poets and scholars such as the linguist Dunash ben Labret and the lexicographer Menahem ibn Saruk. AFter the death of the Caliph, ibn Shaprut serves his successor, Caliph al-Hakim.
950: Count Fernan González wins independence of Castile from Leon. La Poema del Fernan Gonzalez probably written 200 years later.
960: Hasdai ben Shaprut, the personal physician Caliphs Abd-al-Rahman III and Hakam II, and inspector-general of customs and an adviser in foreign affairs, begins a correspondence with Joseph, the Jewish King of Khazaria.
970: Caliph al-Hakaam II founds a library of "hundreds of thousands" of volumes in Cordoba, called "the jewel of the world". With its mansions, mosques, public baths, orchards, courtyards, aqueducts, and half-million people, it is the greatest city of its time. Algebra is invented here, and Arabic numerals and the Indian concept of zero are introduced. More Jews immigrate from the East to this center of learning.
993: Rabbi Samuel Halevi ibn Nagrella (Samuel Ha-Nagid) born in Cordoba.
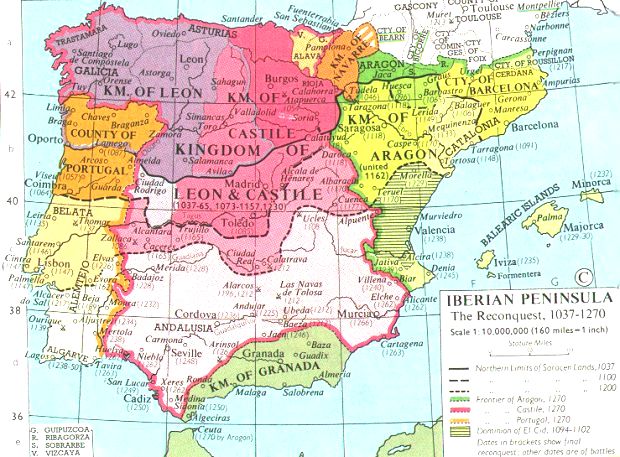
1000 to 1033: Sancho III of Navarre gains control of Aragon and Castile, uniting the three kingdoms. But on his death, he splits the kingdom and leaves Navarre to his son Garcia III, Castile to Fernando I, and Aragon to Ramiro I.
1012: ben Gabirol brings the works of Plato to Spain.
1013: Halevi flees to Malaga when Suleiman attacks Cordoba and destroys cultural center. Halevi becomes vizier to the King of Granada, as does his son, Jehoseph Ha-Nagid. Many other Jews flee to Granada and establish a new cultural center there.
1031: Cordoban Caliphate dissolves into individual Muslim Taifas (petty kingdoms).
1035 to 1063: Fernando I conquers Coimbra and obliges the Muslims of Toledo, Seville and Badajoz to pay him tribute. Before his death, he shares out his territories between his sons: Castile goes to Sancho II and Leon to Alfonso VI.

1040: Las Jarchas, "the first Spanish literature" is produced. Rabbi Shlomo Itzchaki ("Rashi") is born in Troys, France. He will later write an important commentary on the Torah. His writings would be published with the help of his daughters.
1043: Birth of Rodrigo Diaz Vivar, whom the Muslims would name "El Cid Compeador" (Lord Winner of Battles) in Burgos.
1053-1071, Book of Usage written in Barcelona, defining legal status and privileges of Jews. It put the protection of the Jews under the King, who would decide the punishment for any harming or killing a Jew. Castile has similar laws when created.
1058: Conspiracy in the Sotonera.
1065 to 1109: Alfonso VI unites Leon and Castile under his scepter and takes Toledo.
1066: Jehoseph Ha-Nagid and other Jews in Granada are attacked and murdered; many escapees flee to the north. The Normans conquer England.
1085: Toledo captured on May 6 by Alfonso VI, "Emperor of all Spain". Joseph Nasi Ferruziel (called Cidellus)is Alfonso VI’s physician and nasi of all the Jews in the kingdom. He owns large estates in and around Toledo (confiscated by the crown on his death).
1086: The Christian advance obliges the Muslim kings of Granada, Seville and Badajoz to call to their aid the Almoravides ("those vowed to God"), recently converted fanatical Berbers of Africa. Their fanaticism sends some Jews and Christians to the north of Spain.
1092-1167: Rabbi Ben Ezra.
1094-1099: The Cid captures and rules Valencia, pushing back the Almoravides.
1099: Death of El Cid.
11th Century: Jewish merchants introduce the use of shufatajiyya, checks.
1102: The followers of the Cid leave Valencia and the African Muslims occupy the Peninsula as far as Saragossa (Zaragoza). Main Muslim mosque in Toledo converted to a church, Muslim population is sparse. Jews live in southwest coner of the city, "which also contained a fortress".
1118: Alfonso I of Aragon conquers Saragossa, taking it from the Muslims. Settlers in the reconquered no-man's lands of Castile are granted fueros, special rights.
1130: School for scholars is established by Alfonso VII in Toledo, spreading ancient Greek as well as Arabic and Hebrew learning throughout western Europe.

1131: Birth of Rabbi Moses Ben Maimon (called "Rambam" or Moses Maimonides). It is thought that 90% of the world's Jewish population live in Spain.
1140: Poema del Mio Cid written; Rav Yehuda Halevi writes the Kuzari, a philosophical defense of Judaism written in relation to the Jewish kingdom of Khazaria in the far east of Europe.
1144: First case of "blood libel" (accusation that Jews use the blood of murdered Christian children in their ceremonies) recorded in England.
1151: The Almohades, another more conservative African Muslim dynasty who have displaced the Almoravides, retake Almaria. Jews and Mozárabes (Christians in Muslim lands) flee to the northern Christian kingdoms of Spain, or to African and the East, including Rambam. Christian kings in northern Spain use Jews as phyusicians, scientists, tax collectors, judges, diplomats and public officials. Jews are sent by both Muslim and Christian kings to collect tributes from other kindgoms.
1160: Birth of Isaac the Blind, "the father of Kabbalah" in Provence (France).
1171: Almohades Muslims begin building the Alcázar, their magnificent palace.
1172: Benjamin of Tudelo returns from Palestine, having left in 1159. He describs his travels in Sefer ha-Massa’ot (Book of Travels).
1190: Rambam writes the Moreh Nebukhim, or Guide to the Perplexed, using rationalism to reconcile Judaism with Aristotle's laws of nature, and Shloshah-Asar Ikkarim, the Thirteen Articles of Faith.
1205: Death of Rambam (in Egypt). "Birth of Chaiya bat Avraham Toledano" (SCA).
1212: Christians gain control of the peninsula. Alfonso VIII of Castile, Sancho VIII of Navarre, and Pedro II of Aragon (with some troops from Portugal and Leon), are victorious in the battle of Las Navas de Tolosa (the plains of Tolosa).
1213-1276, reign of King James I of Aragon, who encouraged Jews from France and North Africa to settle in Aragon with land and property grants and exemptions from taxes. Many Jews were administers for the royal court, including the manager of the king’s personal property. Solomon and Bahya Alconstantini of Saragossa assist the king in his military campaign. Don Judah ibn Lavi de la Cavalleria becomes the royal treasurer and bailiff of Saragossa in 1257, and controls all crown revenues after 1260.
1215: Fourth Lateran Council institutes the "Badge of Shame", a mark that all Jews are required to wear to distinguish themselves from Christians, and decrees that Jews shall not be seen in public on Good Friday. Fernando III, with the archbishop of Toledo, appeal to the Pope on behalf of the Spanish Jews. The pope, Honorius II, suspends the decision. The Magna Carta is written in England.
1217 to 1252: Fernando III, king of Castile and Leon, conquers Cordova, Murcia, Jaen and Seville. Granada remains as the sole independent Muslim kingdom. "España" begins to be thought of as all of Spain, not just Muslim Spain.
1228: King James I fixes 20 percent maximum interest on loans; decrees that a Jewish oath can not serve as evidence in a court of law. Alfonso X fixes 33.3% interest, and establishes the Rab de la Corte or chief justice of appeals (rabbi) in Las siete partidas.
1238: Birth of Moses de Leon, who published Sepher ha Zohar or "Book of Splendor", one of the most influential Kabbalistic document, which some Jewish communities value as an important source of interpretation on the Torah.
1242: As anti-Semitism rises in central Europe, the Talmud is burned in Paris.
1243: University of Salamanca founded.
1244: Tartars capture Jerusalem.
1248: Christian armies under Ferdinand III take Seville after 16 months of seige, despite Muslim catapults, Greek fire, and bowmen who pierce armor.
1250: First recorded Spanish "blood libel" case Saragossa. Toledo becomes a center for Kabbalah studies, until 1325. Nachimonides (perhaps) writes Sacred Book, "essentially a Jewish marital manual" (Yaakov HaMizrachi).
1252 to 1284: Alfonso X the Wise continues the Christian conquest of the peninsula and is obliged to face the 'Mudejar' revolts of Andalusia and Murcia. He seeks election as emperor of the Holy Roman Empire in 1257. He drafts the Fuero de las Leyes' the forerunner of the 'Siete Partidas'.
1263: July 20-23, the Barcelona Disputation, "religious disputation between Pablo Christiania and Nahmanides of Gerona in the presence of King James I."
1265: Las Siete Partides, Alfonso X's law codes, which include a section "Concerning the Jews".
1267: Nahmanides flees to Eretz Israel for safety.
1284: An assembly of nobles, prelates and citizens depose Alfonso X and hand over power to his son Sancho IV.
1290: All Jews are expelled from England. Many move to Spain.
1304: Rav Asher moves to Spain.
1306 - Jews expelled from France move to Barcelona and Toledo. Includes Estori ha-Parhi (1280-1355?), topographer of Eretz Israel.
1355 - Henry of Trastamara, half-brother of King Peter the Cruel of Castile, vies for the throne. He declares that he is trying to free Castile from the harmful influence of the king’s Jewish advisors. In the spring of 1355 his forces attack the small Jewish quarter of Alcana in Toledo and loot the smaller Jewish quarter, killing more than one thousand Jews, according to contemporary historian Pedro López de Ayala. The larger quarter is protected by hired mercenaries. In 1366 Henry entered Toledo and demanded one million maravedis to ransom the Jewish quarter; the Jewish community sell the Torah crowns to pay.
1348: The Black Death strikes central Europe, then Spain. Almost 40% of the total population eventually dies. However, some Jewish communities are spared since the Torah requires that Jews wash before eating bread, bathe before the Sabbath, and recite blessings and study the Torah at a distance from sewage. The dead, also, must be buried quickly. Unknown to the Medieval person, these measures help to prevent disease. However, this only causes Christian plague sufferers to accuse Jews of having brought the Plague or of poisoning their wells.
1350: Peter the Cruel takes the throne. His treasurer is Samuel Levi of Toledo and his physician is also Jewish. Jewish taxes to the king make up half of the royal revenue in some areas, representing more than their proportion of the population.
1391: Persecution of the Jews lead to riots, thefts of Torahs, and seizures of synagogues, which are later converted to churches. Thousands of Jews are killed. June 4, anti-Jewish riots break out in Seville and spread through most of Spain, with clergy, nobles, townsfolk and peasants participating. The king of Aragon inherits the property of Jews without heirs killed in the riots.
1394: Jews expelled from France. Many move to Spain.
1413-14: Jewish delegates are set up to fail in a debate between Jewish and Christian theologians at Tortosa. Thousands of Jews convert to Christianity. Some continue to practice Judaism in secret; these are called "marranos" ("pigs" or "swine", a great insult to a Kosher person!) by the Spanish.
1440s: Gypsies enter Spain (from Egypt) and end up preserving the Andalusian cante jondo (traditional songs) and baile flamenco (traditional dances) into the 20th Century.
1464: Enrique IV of Castile names as heir to the throne his sister, the future Isabel I, the Catholic, and disinherits his daughter Juana.
1469: Isabel I of Castile and Fernando II of Aragon are married, thus consummating the unity of Spain. Jews involved in the court help to arrange the marriage, in the hope that a unified, peaceful Spain will bring greater prosperity and safety to Sephardic Jews.
1473: First printing press in Spain.
1478: The New Inquisition begins to seek out "marranos" (Jews secretly practicing Judaism after publicly converting to Christianity) and heretics by using torture on "conversos" or "New Christians".
1492: The Catholic Monarchs, Isabel and Fernando, conquer Granada (January 2nd), taking advantage of the rivalry of the last Muslim governors of Spain. All Spanish Jews are expelled from Spain on the 9th day of the Jewish month of Av (the first week of July), the anniversary of the destructions of the Temple in Jerusalem. Discovery of America (October 12th), by Christopher Columbus, who may have been Jewish.